Natural Antibacterial Product Series


| Solution Type | Features |
|---|---|
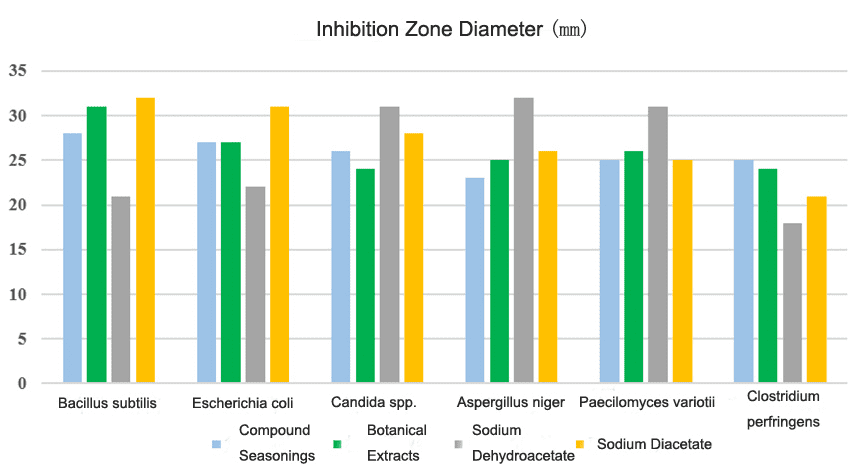
| Compound Seasonings | 1. Fermentation products contain various organic acids, offering a broad antibacterial spectrum. 2. Developed in collaboration with renowned domestic university research institutes using high-quality, safe, and healthy bacterial strains. 3. Mild taste, does not affect product flavor. |
| Plant Extracts | 1. Ingredients sourced from nature, green and healthy. 2. Enhances aroma and flavor while providing certain antibacterial effects. |
Antibacterial Mechanism
Antibacterial Data Product Categories
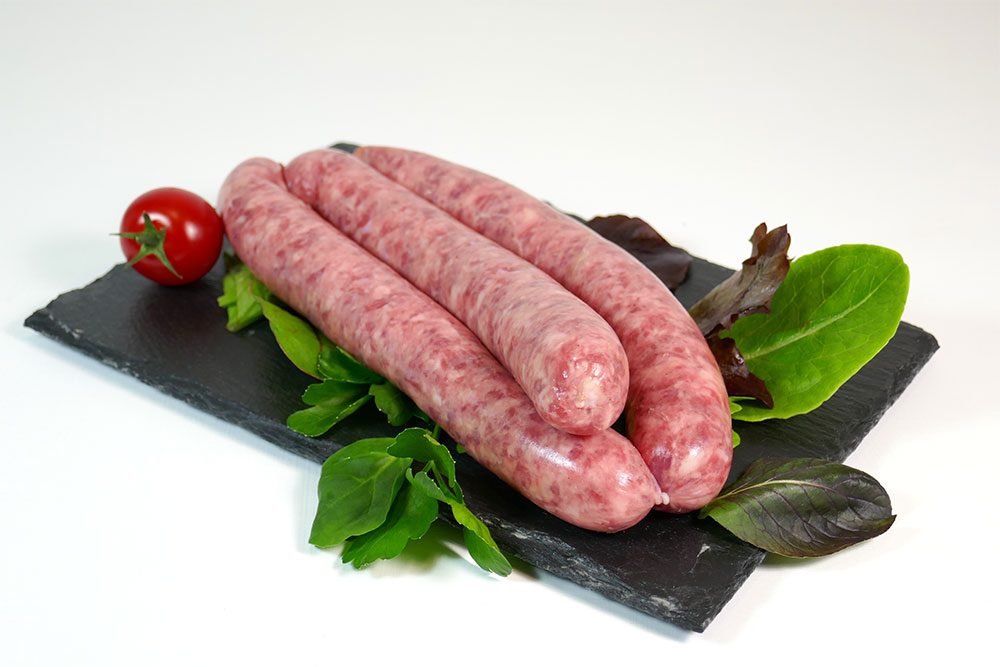
Cooked Meat Products
Starch Products
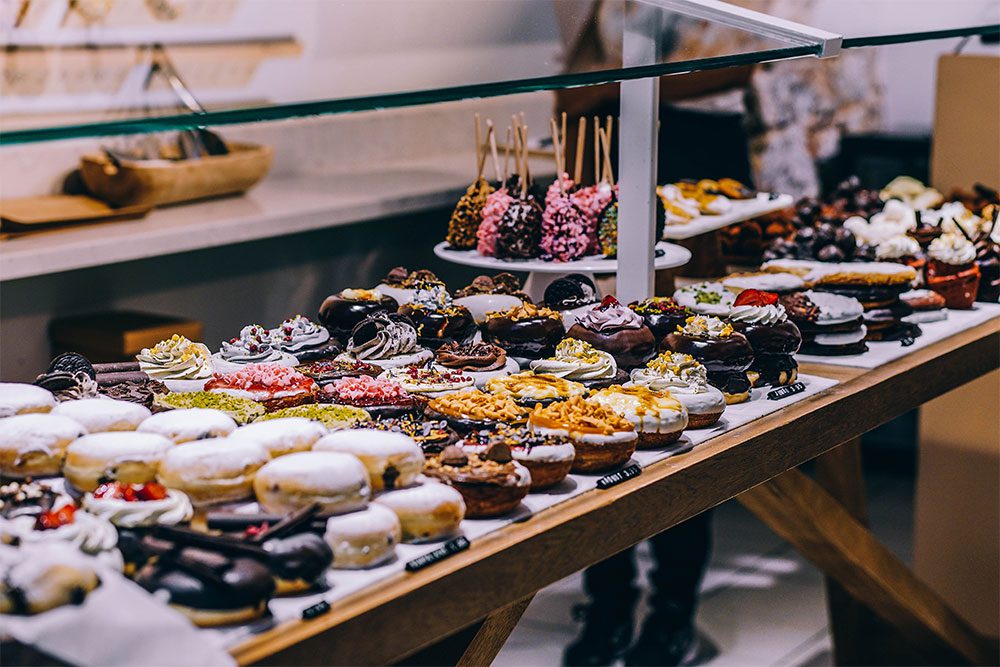
Bakery Products
Rice & Noodle Products
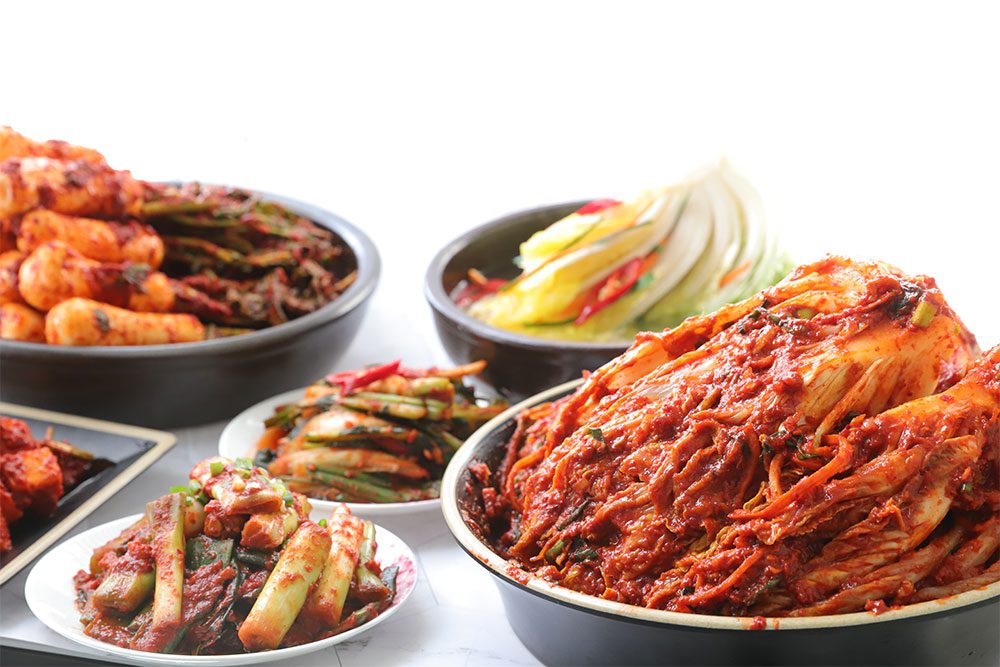
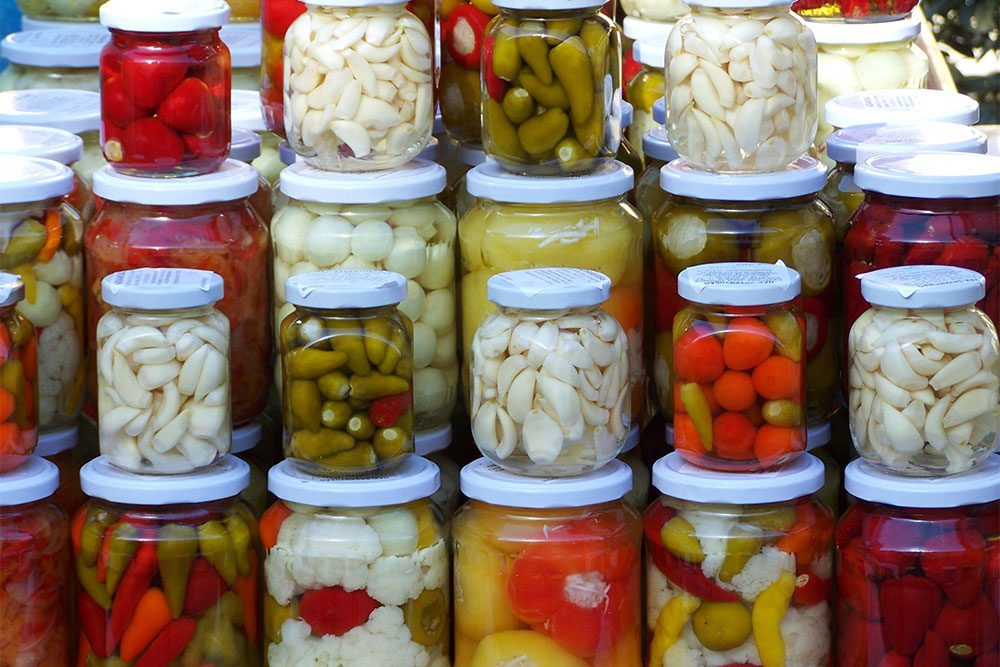
Pickled Vegetable Products
AW-55 Natural Preservative


- Principle: Achieves preservative effect by reducing water activity (By lowering water activity, it converts free water, separated water, and unbound water into bound water, reducing the free water available for microbial growth and disrupting their nutrient supply for reproduction, thus achieving preservation).
- Product Description: (AW-55) This product is primarily extracted from natural raw materials, using lactic acid as a base and compounded with the latest high-tech blending technology. It is also an excellent natural preservative and freshness agent. This product helps maintain product palatability and provides excellent moisture retention, freshness preservation, and color protection.
- Usage Method:
- Recommended dosage: 4% ~ 5% (calculated based on the total weight of water and filling).
- Add during tumbling or chopping processes.


- Successful Product Case Examples:
Water Activity and Food Safety
- Definition of Water Activity:
Water activity refers to the state of water in food, i.e., the degree of binding between water and the food matrix. The lower the degree of binding, the higher the water activity value; the higher the degree of binding, the lower the water activity value. - Methods to Reduce Water Activity:
Water exists in two states in products: free water and bound water. Free water is in a separated, or unbound state. By converting free water, separated water, and unbound water into bound water, water activity can be reduced. This minimizes the free water available for microbial growth and disrupts their nutrient supply, achieving preservation. Water activity is a critical factor determining the shelf life of a product. - Relationship Between Water Activity and Microbial Growth:
While water activity cannot predict food safety after freezing, it is closely related to the safety of unfrozen foods. Water activity is a key factor determining shelf life. When temperature, pH, and other factors favor rapid microbial growth in a product, water activity can be the most important factor controlling spoilage. The general trend is that foods with lower water activity are more stable and less prone to spoilage.
Specifically, the relationship between water activity and food safety can be outlined as follows from the perspective of microbial activity:
Different types of microorganisms require a certain level of water activity for growth. In other words, specific microorganisms can only grow when the food’s water activity is above a critical threshold. Generally, for most bacteria it is 0.94~0.99, for most molds it is 0.80~0.94, for most halotolerant bacteria it is 0.75, and for xerotolerant molds and osmotolerant yeasts it is 0.60~0.65. When the water activity falls below 0.60, the vast majority of microorganisms cannot grow.
Summary